Explain Why Boron Atoms Can Be Similar and Different
So boron -11 has five protons the same as boron-10. If the AuCu alloy is harder than the AuAg alloy then which of the following is the best explanation based on the information in the.

Brand New Bonding Skills Make Boron More Like Carbon New Scientist
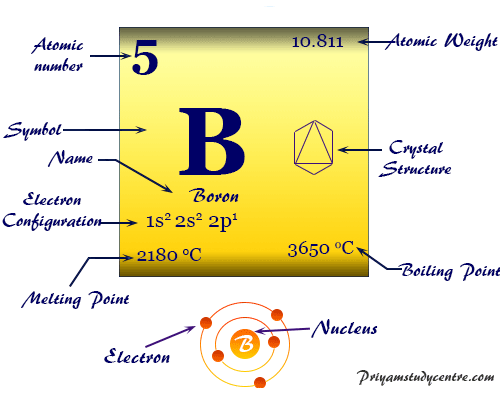
We are given that boron-10 had five protons in its nucleus and any element always has the same number of protons in its nucleus atomic number.

. σ orbitals are end-to-end combinations of atomic orbitals whereas π orbitals are formed by side-by-side overlap of orbitals. The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. Only small amounts of wurtzite boron nitride and lonsdaleite exist naturally or have been made in the lab so until now no one had realised their superior strength.
These are from 2 different periods on the Table of Elements and have different properties. So it is a 3D giant covalent lattice. Than or the same as the atomic radius of 87Rb.
Moreover boron nitride is an excellent thermal and chemical resistant refractory material while graphite has excellent electrical conductivity. This is similar to ammonia NH3 plus boron trifluoride BF3 yielding NH3BF3. A covalent network is a compound composed of a continuous network throughout the material in which the atoms are bonded to each other via covalent bonds.
Hence it can form only three covalent bonds which means only six electrons are present around the boron atom and its octet remains incomplete. Both are bonding orbitals that can contain a maximum of two electrons. It has three electrons in its valence shell.
Atoms and Atomic Structure. The first wurtzite boron nitride has a similar structure to diamond but is made up of different atoms. The key difference between ammonia and boron trifluoride is that ammonia is a polar molecule whereas boron trifluoride is a nonpolar molecule.
The list is Hydrogen Helium Lithium Beryllium Boron and Carbon. It can achieve this chemistry because boron really does have two sides to it - it is set up to form 3 bonds with adjacent atoms but even in this state readily forms an extra bond in order to complete the 2 nd main shell of 8 electrons. Predict whether an atom of 88Sr will have an atomic radius that is larger than smaller.
But when it does this it acquires a negative charge and it can only regain neutrality by losing one of its bonds - it really does have a split personality. Here boron-11 means the name of the element is boron and the mass number is 11. The outer electron in boron is in a higher energy 2p subshell which making it easier to loss an electron.
Isotopes are given by the name of the element and the mass number. In fact it is isoelectronic with the giant covalent lattices of carbon. To make Au stronger and harder it is often alloyed with other metals such as Cu and Ag.
Ammonia and boron trifluoride have similar atomicity and closely similar connectivity of atoms but there is a lone electron pair on the nitrogen atom in ammonia molecule while there are no lone electrons on the boron. Different solids have different shapes and volumesDifferent solids have different. The following table summarizes the difference between boron.
How can you tell the difference between a covalent molecular and covalent network. When one atom of boron combines with three atoms of fluorine its octet remains incomplete. The key difference between boron nitride and graphite is that boron nitride is composed of boron and nitrogen atoms whereas graphite contains carbon atoms.
Hence boron trifluoride remains electron-deficient and acts as a Lewis acid. In the cubic form of boron nitride alternately linked boron and nitrogen atoms form a tetrahedral bond network exactly like carbon atoms do in diamond. Can boron nitride conduct electricity in solid state.
The term covalent molecular is used to explain molecules that are formed by covalent bonding. Therefore the number of electrons in neutral atom of Boron is 5. Consider two alloys one of Au and Cu and one of Au and Ag each with the same mole fraction of Au.
Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other Z 1 negative electrons in the atom.

Brand New Bonding Skills Make Boron More Like Carbon New Scientist

No comments for "Explain Why Boron Atoms Can Be Similar and Different"
Post a Comment